Benefits of ISO Standardization to the ENFit® Enteral Feeding Connector
Tubing misconnections continue to cause severe patient injury and death, since tubes with different functions can easily be connected using luer connectors, or connections can be “rigged” (constructed) using adapters, tubing or catheters. This is why new ISO (International Organization for Standardization) tubing connector standards are being developed for manufacturers.
ISO80369 White Paper ISO Guideline for the implementation of medical products using small bore connectors specified in the ISO-80369 series
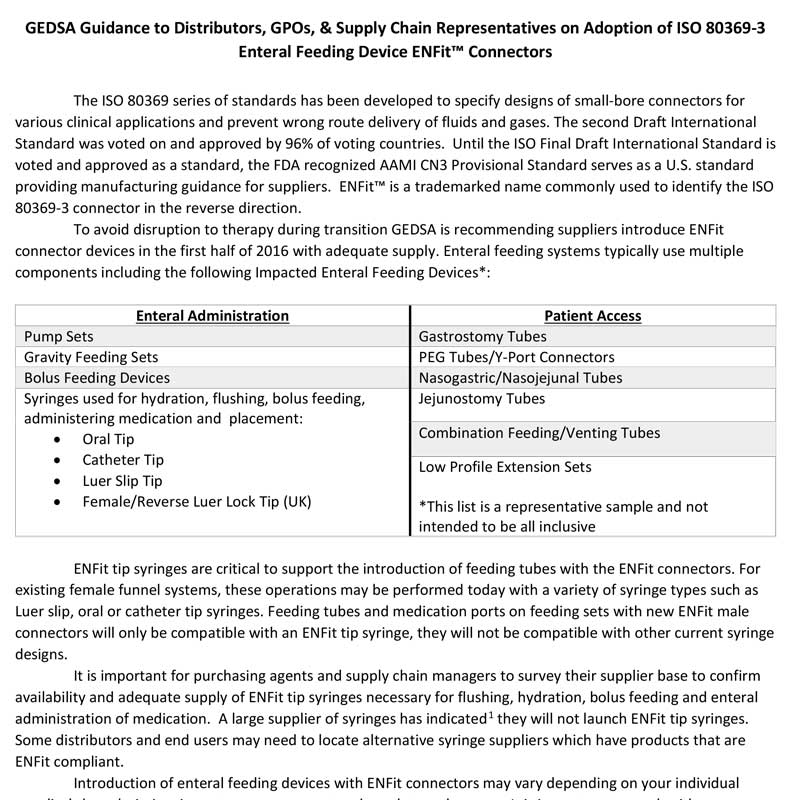
GEDSA Guidance to Distributors, GPOs, & Supply Chain Representatives on Adoption of ISO 80369-3 Enteral Feeding Device ENFit™ Connectors
Subject Line: The FDA Encourages Use of Enteral Device Connectors that Reduce Risk of Misconnection and Patient Injury Dear Colleagues, The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is concerned by continued reports of misconnections with enteral devices. To reduce the risk of misconnections and patient injury, the FDA recommends hospitals and clinicians use enteral devices with connectors that meet the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 80369-1 or ISO 80369-3 standard, or that are otherwise designed to reduce the risk of misconnections. There are currently marketed enteral connectors that meet the 80369-3 standards, many of which are identified by the tradename ENFit.
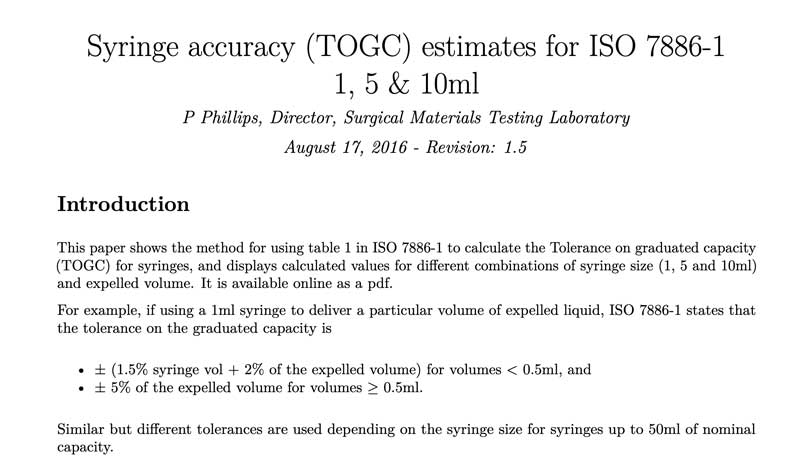
This paper shows the method for using table 1 in ISO 7886-1 to calculate the Tolerance on graduated capacity (TOGC) for syringes, and displays calculated values for different combinations of syringe size (1, 5 and 10ml) and expelled volume. It is available online as a pdf.
November 2016: GEDSA Position Statement in support of ISO 80369-6 To reduce the risk of wrong route delivery of fluids and gases (tubing misconnections) there is an ongoing effort led by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) to address smallbore connectors for healthcare applications.